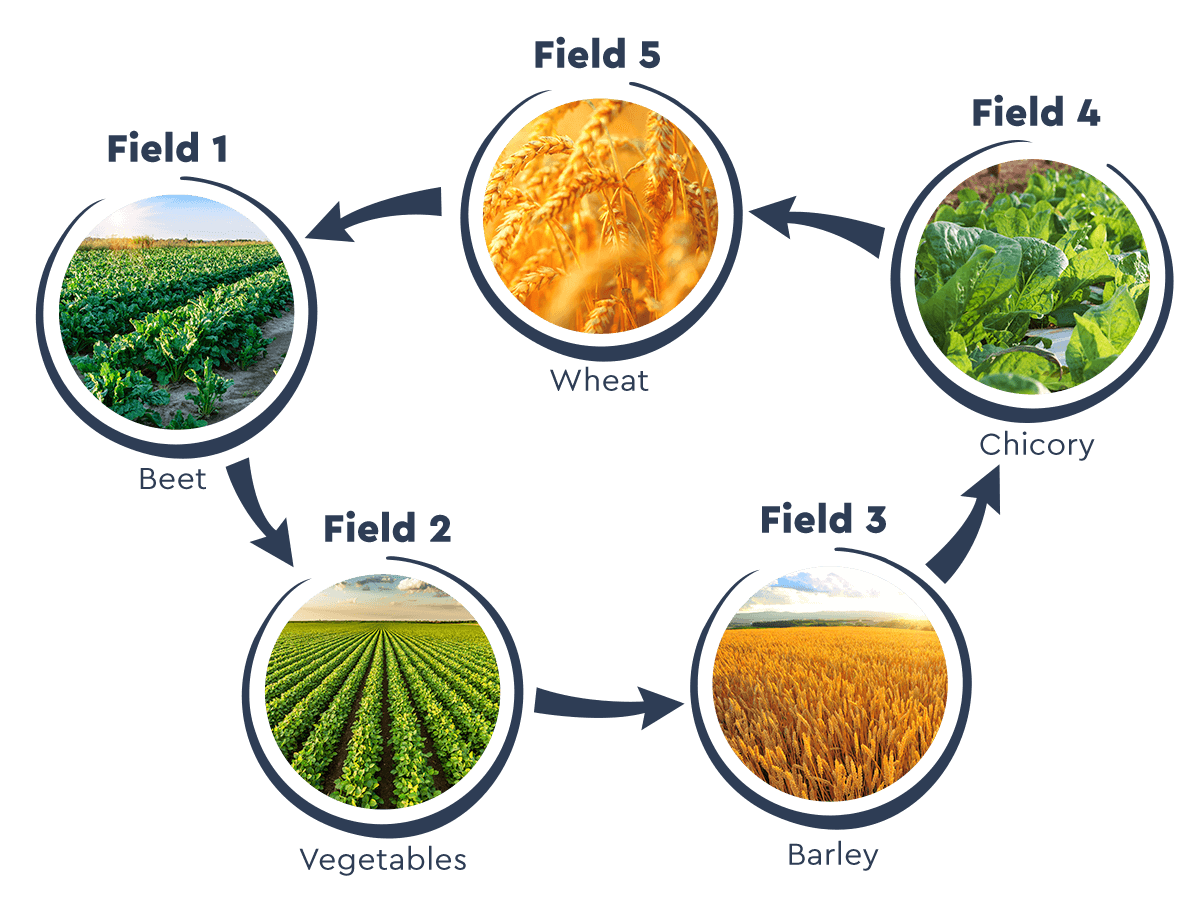
Sustainable agriculture is an ecologically and socially responsible approach to farming that focuses on preserving natural resources and promoting long-term agricultural viability. It emphasizes practices that maintain soil health, conserve water, and protect biodiversity while ensuring economic profitability for farmers. By employing techniques such as crop rotation, organic farming, and integrated pest management, sustainable agriculture minimizes environmental impact, reduces reliance on chemical inputs, and supports resilient and diverse ecosystems. Additionally, it promotes social equity by fostering fair labor practices, supporting local communities, and encouraging active engagement among farmers. Sustainable agriculture serves as a crucial framework for meeting current food needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own, creating a balanced and sustainable future for agriculture.